Electrical Help
110-220 Switch Wiring
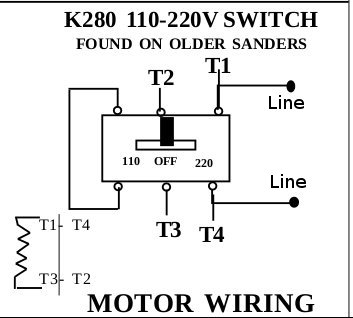
The 110-220 selector switch found on many of the older drum sanders is a 3-position, snap action switch (Part # K280). Below is a diagram to wire this switch.
Capacitors
If you have an American Sanders machine with a Baldor motor, check out our wiring video here: https://youtu.be/f5yxljpCM2Q
Overview
Capacitors are used on most modern sanders & buffers. Traditionally, motors are either brush type or induction type. Induction motors have capacitors, brush motors do not. There are a few exceptions: the old Portercable motors were brush start, induction run. These used a finger mechanism to short out the bars on the armature once the motor was running. There are also modern motors that are neither brush nor induction. These are called Switched Reluctance, and are found on some vacuum motors, the Bona Advantedge, and the KT RTA buffers. These use a complex control circuit and electrical pulses.
Capacitors generally have 2 ratings: voltage and capacitance. The voltage rating is the maximum voltage. This is not important as long as it is greater than the machine voltage. The capacitance is measured in microfarads, often displayed as mfd or uF. In many cases this is a range, such as 460-552mfd.
Motors will normally have a run capacitor and one or two start capacitors. The run capacitor is normally metal, and has a lower rating, while the start capacitor(s) will be plastic and have a higher rating. European made machines are the exception - they will have both capacitors metal or plastic. The start capacitor, as its name suggests, is only used to start the motor. It is then switched out of the circuit when the motor is up to speed. This is normally done one of three ways:
- A manual switch, such as is used on Hummel sanders. This switch must be manually turned to start, then released when the motor is up to speed.
- A centrifugal weight system and a contact switch. This is commonly found on older motors. When the motor gets up to the required speed, the weights release the switch to disengage the start circuit, and engage again when the motor slows back down.
- A sinpac switch. This is an electronic switch that engages and disengages the start circuit automatically based on motor voltage. These are used on most modern buffers & alto sanders.
Diagnosis
Most motor problems on modern machines are related to the capacitors. One important thing to remember when working with capacitors is that capacitors will hold a charge even when disconnected. It is recommended that you discharge this voltage by shorting the terminals with a resistor for a few seconds before handling the capacitors.
When a motor has trouble starting, or does not try to start at all, this is normally a problem with the start capacitor or the start switch. Remember, if your motor has 2 start capacitors, one may be bad and the other not. This will cause it to start slower. On machines with a sinpac switch, running with too long a power cord (over 100 ft) may cause the switch to keep cycling on and off. This is due to the low voltage - the switch operates by sensing the voltage. If the voltage gets down to 192 volts, it will turn on the start circuit. You will generally not notice this, but the capacitor and start switch will get hot and stop working. On some motors, the start windings may also be damaged.
When a run capacitor is bad, the motor will generally still run. However, it will lack power and run hot. The current draw will also increase, so it may trip circuit breakers. Most induction motors will draw less than 5 amps with no load; with a bad run capacitor, it will draw 10-15 amps.
Testing
To test the capacitance of a capacitor requires a special meter. However, this is not important. When capacitors go bad, they usually get a short or open circuit. This is easy to test with an ohm meter.
An analog meter works best, but a digital meter can be used if necessary. First, discharge the capacitor with a resistor. Next, disconnect the wires from the capacitor. Set your meter at a high setting (200K ohms is fine). Put one lead on each terminal. The meter should start at a low resistance reading, and increase until it reaches infinite. It does this because the capacitor is absorbing the power from your ohm meter. The resistance of the capacitor increases as it charges up. The capacitor will now be charged up; discharge it before reconnecting the terminals.
If your meter showed 0 and stayed there, your capacitor is shorted. If it showed infinite from the start, it is either open or you forgot to discharge it. Whether your capacitor is open or shorted, it needs to be replaced.
Replacement
It is recommended to replace capacitors with one of the same value. Using a different size capacitor will change the motor's current draw and torque, and may cause the motor to overheat. Always use the correct size capacitor.
A chart of the capacitors we stock is provided below.| Part # | Rating (MFD) | Notes |
| AS73 | 20 | |
| BA56 | 25 | |
| WS206 | 35 | |
| CL40 | 40 | |
| HS205 | 40 | With mounting stud |
| HSSWR | 40 | |
| BB153 | 50 | With wires |
| GAL032 | 50 | |
| TS205 | 50 | With wires |
| TS205US | 50 | |
| EZ68 | 60 | |
| WS205 | 60 | |
| BB205 | 80 | With wires |
| TS153 | 100 | With wires |
| TS153US | 100 | |
| HS153 | 130 | With mounting stud |
| HSSWS | 108-130 | |
| CL39 | 161-193 | |
| GAL030 | 216-259 | |
| B03 | 340-408 | |
| BA63 | 460-552 | |
| EZ69 | 645-774 | |
| AS74 | 704-845 | |
| WS153 | 708-850 |
